Mục Lục
As businesses and technologies evolve in the digital economy, tokenization meaning has become a crucial term across various industries. Whether you’re in finance, cybersecurity, blockchain, or eCommerce, understanding tokenization meaning is vital for protecting sensitive data and optimizing digital operations.
In this article, we’ll explore the full tokenization meaning, why it matters, how it works, and its applications — especially in asset tokenization and payment tokenization. Let’s dive in.
What is Tokenization?
At its core, the tokenization meaning refers to the process of converting sensitive data into unique, non-sensitive equivalents known as tokens. These tokens can be used in place of real data without exposing the original information, helping reduce the risk of breaches or data misuse.
In simple terms, tokenization helps secure information like credit card numbers, bank details, or identity credentials by replacing them with randomized tokens that are useless if stolen.
Tokenization Meaning in Different Contexts
The tokenization meaning varies depending on the industry. In cybersecurity, it’s about data protection. In blockchain, it refers to the creation of digital tokens that represent real-world assets.
- In payment tokenization, your credit card number is replaced by a token during transactions, reducing fraud risk.
- In asset tokenization, a real-world asset like real estate, gold, or intellectual property is converted into a digital token on a blockchain.
Understanding tokenization meaning in these distinct areas helps you grasp the full power and versatility of this technology.
Xem thêm: https://dk-tech.vn/token-va-coin-co-gi-khac-nhau/
Why Tokenization Matters
The reason tokenization meaning is increasingly relevant today is because of growing concerns over data privacy, fraud, and the digitization of traditional assets. With tokenization, businesses can:
- Enhance data security
- Comply with privacy regulations (GDPR, PCI-DSS)
- Improve user trust
- Enable decentralized finance (DeFi) innovations
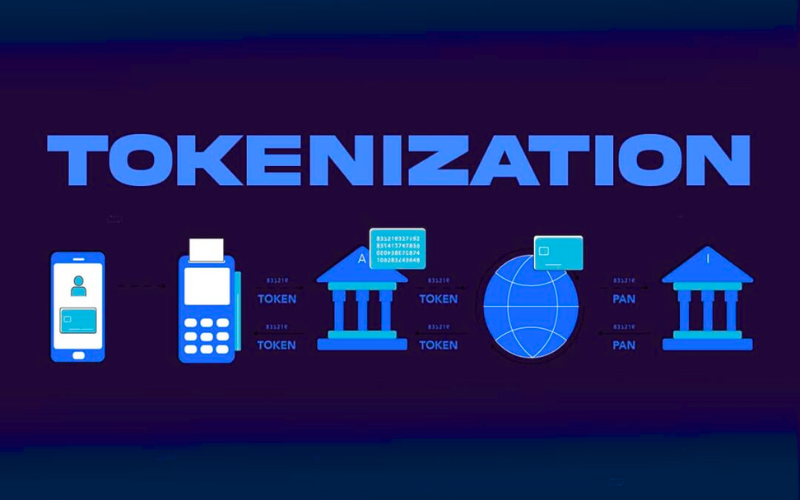
The Tokenization Process Explained
To understand tokenization meaning better, let’s break down the tokenization process:
- Data Input: The original sensitive information is collected (e.g., credit card number).
- Token Generation: A random token is generated to replace the original data.
- Storage: The real data is stored securely in a token vault.
- Usage: The token is used in systems and applications without exposing the original information.
This tokenization process ensures that even if the token is intercepted, it is useless without access to the token vault.
Use Cases of Tokenization
1. Payment Tokenization
Payment tokenization is one of the most widespread uses. Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and online payment gateways rely on tokenization to replace actual card data with secure tokens during transactions.
2. Asset Tokenization
Asset tokenization allows businesses and individuals to digitize ownership of physical assets, enabling fractional ownership, global trading, and increased liquidity. Real estate, artworks, and even stocks can be tokenized, revolutionizing investment models.
3. Blockchain and Crypto
In blockchain, tokenization meaning extends to creating digital representations of anything valuable — be it a utility token, a stablecoin, or a security token. These tokens can then be traded, staked, or integrated into decentralized applications (dApps).
Benefits of Tokenization
Understanding the true tokenization meaning also means recognizing its advantages:
- ✅ Enhanced data privacy
- ✅ Reduced compliance risks
- ✅ Improved scalability
- ✅ Safer digital payments
- ✅ Democratized asset ownership
Tokenization Meaning vs Encryption
While both techniques protect data, tokenization and encryption serve different purposes. Encryption can be reversed with a decryption key, while tokenization replaces data entirely and stores the real data separately, making it more secure in many cases.
Future Trends in Tokenization
As the digital world continues to evolve, the tokenization meaning will expand. With the growth of Web3, NFTs, and decentralized finance, tokenization is paving the way for new innovations in identity management, smart contracts, and global trading systems.
Conclusion
By now, the tokenization meaning should be clear: it’s a powerful tool that transforms how we handle, protect, and interact with data and assets in the digital age. Whether in the form of payment tokenization, asset tokenization, or the overall tokenization process, this technology offers scalable solutions for modern challenges.
If you’re planning to build secure digital platforms, understanding the tokenization meaning is no longer optional — it’s essential.
>>> Khám phá: Dịch vụ thiết kế Token
What are examples of tokenization?
Tokenization is commonly used in financial and digital systems to protect sensitive data. For example, when you use a payment app like Apple Pay, your actual credit card number is not stored or transmitted. Instead, the system generates a random token (such as 5467-–-8821) to represent your card. This token is meaningless if stolen and can only be used in the specific context it was created for. Other examples include tokenizing customer names, Social Security numbers, or bank account numbers in databases to protect personal identity.
What is tokenization in mobile payments?
In mobile payments, tokenization refers to the process of replacing your real payment card details with a digital token. When you add your card to a mobile wallet (like Google Pay, Samsung Pay, or Apple Pay), a unique token is created to represent your card during transactions. This means the actual card number is never shared with merchants or stored on the device. Even if someone intercepts the transaction, they can’t use the token to access your real card details, which significantly reduces fraud risk.
What is tokenization in digital banking?
In digital banking, tokenization is used to secure sensitive financial data such as account numbers, customer IDs, or authentication credentials. Instead of transmitting or storing actual data, the system uses tokens to represent that information during online transactions or mobile banking activities. This makes it much harder for cybercriminals to access or misuse customer data. Tokenization in digital banking enhances data privacy, supports regulatory compliance, and builds user trust in digital platforms.


